
The very first life form on earth. What was it? What did it look like? When did it appear? How did it come to be? These are all very good questions. Questions which are usually answered with more imagination than actual science since we weren’t there to observe of course. But the biggest question has to be the “how.” It is the “how,” that plagues the scientist’s mind when it comes to the first life.
There are only two means by which the first life could have appeared: natural origins or supernatural origins. Natural origins means the life came from non-living chemicals. Supernatural origins means the life came from an Intelligent Designer, a Creator God. Now immediately science throws out supernatural origins because it is of course not natural, and therefore, in the minds of most scientists, not science. Yet science itself cannot seem to yield any satisfying answers to the origin of life on earth. If life came from non-life, this brings with it a wide variety of problems and dead ends.
The Environment Problem
As much as we understand this planet to be hospitable for life, it is only hospitable for life fitted to live on it. For example, oxygen and water are required for life to exist, but are also detrimental to the internal components of an organism.
Let us take oxygen for example: It is a poisonous gas that oxidizes organic material.[1] The only way organisms can tolerate it is because they are already capable of tolerating it, with membranes that protect oxygen from damaging internal components of the cell. Therefore there is no way the organisms could have evolved from non-living material unless protective membranes were already present to protect the vulnerable internal organelles from oxidization. What are the odds that the first life form ever just so happened to have a protective membrane already in place?
Some evolutionists argue that this is not a problem because it assumes oxygen was not present in the early atmosphere of earth, and therefore not a threat. But the evidence does not support this claim. Even earth’s oldest rocks contain evidence of formation in an oxygen rich atmosphere.[2] Atmospheric physicists believe the earth has been fully oxidized for at least 4 billion years.[3] A fairly recent article published on crystals dated to 4.4 billion years ago show heavy evidence of oxidation.[4] Additionally, oxygen is needed for life as protection from harmful UV rays which we have via from the ozone layer, which is made out of oxygen![5] If there was no oxygen UV rays would eradicate all early life forms. Biochemist and molecular biologist Michael Denton writes, “What we have is sort of a ‘Catch 22’ situation. If we have oxygen we have no organic compounds, but if we don’t have oxygen we have none either.”[6]
To get around this concern of oxidization, scientists propose life formulated in the oceans and therefore was not subjected to oxygen initially. But just as with oxygen, water is hazardous to life as well. Organic molecules would be destroyed through the process of hydrolysis (also called “water splitting”) in which water bonds between two molecules causing them to split apart.[7] Any amino acid trying to form a protein would have its bond broken in a short matter of time. The US National Academy of Sciences confirms, “In water, the assembly of nucleosides from component sugars and nucleobases, the assembly of nucleotides from nucleosides and phosphate, and the assembly of oligonucleotides from nucleotides are all thermodynamically uphill in water. Two amino acids do not spontaneously join in water. Rather, the opposite reaction is thermodynamically favored at any plausible concentrations: polypeptide chains spontaneously hydrolyze in water, yielding their constituent amino acids.”[8] Physicist Richard Morris concurs, “… water tends to break chains of amino acids. If any proteins had formed in the ocean 3.5 billion years ago, they would have quickly disintegrated.”[9] Thus, the first life form would have needed a protective membrane already in place to protect it from oxygen and water. Yet, where did this membrane come from?
Additionally, the cytoplasm of living cells contain essential minerals of potassium, zinc, manganese and phosphate ions. If cells manifested naturally, these minerals would need to be present nearby. But marine environments do not have widespread concentrations of these minerals.[10] This has lead researchers to propose that life originated not in oceans, and not in locations exposed to oxygen, but instead in geothermal pools, geysers and mudpools, much like the primordial soup Darwin proposed. Yet all these geothermal features have one thing in common: They are incredibly acidic.[11] They also tend to be very hot, which would destroy many vital amino acids.[12] How did the cell develop protection from this acidity and from this heat? Without such protection initially it could have never come together.
Some speculate that natural selection of non-living chemicals provided such protective features. This is, however, a common error some scientists make in this arena when they propose natural selection occurred for these protective systems to be in place. As Chemist Dr. Jonathan Sarfati points out, “…when it comes to the origin of first life, natural selection cannot be invoked, because natural selection is differential reproduction. That is, if it worked at all, it could only work on a living organism that could produce offspring. By its very definition, it could not work on non-living chemicals. Therefore, chance alone must produce the precise sequences needed, so these simulations do not apply.”[13]
A significant problem with proposing life arose spontaneously via natural means is that in order to do so, the components of the cell would have to be naturally nearby. In other words, the cell’s chemical makeup would have to be harmonious with the environment’s chemical make up. UniversityCollegeof Londonbiochemist Nick Lanepoints out the problem with this, “To suggest that the ionic composition of primordial cells should reflect the composition of the oceans is to suggest that cells are in equilibrium with their medium, which is close to saying that they are not alive. Cells require dynamic disequilibrium — that is what being alive is all about.”[14] This is a tough fact to accept, but undoubtedly true. How could the first life form have naturally manifested via chemical means with a chemical make up so different and unique from the environment it is within?
The Homochirality Problem
Moving forward brings forth a new set of problems when amino acids are discussed. Often amino acids are discovered in locations where it is suggested they are naturally produced (like being found in meteorites). When this happens there is usually a hype of excitement over uncovering the source of the origin of life via natural means. But simply having amino acids around doesn’t solve the origin of life problem. There is an issue of handedness with amino acids. Out of the twenty amino acids used for life, the atoms that build them formulate two different shapes; right handed and left-handed amino acids. Just like a human hand, they’re slightly different. Your thumb is on the left side on one hand, but on the right side on the other. Amino acids are likewise mirror images of each other and are therefore called chiral.
But this creates a problem. Just like hands clasping together, right and left handed amino acids want to bond, canceling each other out. Yet, the amino acids found in proteins are 100% left handed, where as right handed amino acids are never found in proteins![15] Research indicates that right handed amino acids could never form a functioning protein. The fact that only left handed amino acids can create life is called homochirality. Yet any natural process of creating amino acids would create and equal amount of both left handed and right handed amino acids called racemates.[16]
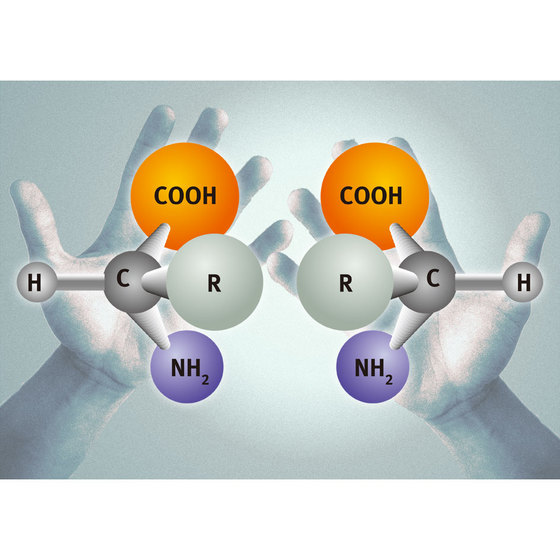
One of the most influential chemist/biochemists of the 20th century, Linus Pauling, writes, “This is a very puzzling fact… All the proteins that have been investigated, obtained from animals and from plants from higher organisms and from very simple organisms- bacteria, molds, even viruses- are found to have been made of L-amino acids.”[17] This is puzzling of course because what natural process only produces one type of amino acid, and not the other amino acid detrimental to life? The late Robert Shapiro, professor emeritus of chemistry at New York University writes, “The reason for this choice [only L-amino acids] is again a mystery, and a subject of continued dispute.”[18] Biochemist and head of the Department of Nuclear Medicine and Director of Clinical Research at the Singapore General Hospital, Dr. Aw Swee-Eng, is more direct on the subject, “The logical conclusion from these considerations is a simple and parsimonious one, that homochirality and life came together. But evolutionary lore forbids such a notion. It claims to explain how life began, but on the profound issue of life’s “handedness” there is no selective mechanism that it can plausibly endorse.”[19]
The Concept of Information
One factor that is sometimes left out in origin of life talks, that is in my opinion, critical, is the concept of information. All living organisms contain within their DNA information, and not just a little, but a lot! Former physics professor and director of information processing at the Instituteof Physicsand Technology in Braunschweig Germany, Dr. Werner Gitt, writes, “The highest known (statistical) information density is obtained in living cells, exceeding by far the best achievements of highly integrated storage densities in computer systems.”[20] This information leads to highly efficient bio-machinery in our cells that complete a vast array of functions. Every biological function that occurs can be traced back to proteins from genes from reading and transcribing RNA that receives the instructions from the information stored in DNA. It doesn’t simply just happen. It is an immensely complex, sophisticated and detailed process occurring non-stop and very rapidly. In fact, the average cell produces a protein through these processes every four minutes.[21]
Any theory or hypothesis to how life originated naturally must take the source of this information into account. Yet, none can be found. Gitt writes, “There is no known law of nature, no known process and no known sequence of events which can cause information to originate by itself in matter.”[22] Biologist Dr. Raymond Bohlin writes, “DNA is information code… The overwhelming conclusion is that information does not and cannot arise spontaneously by mechanistic processes. Intelligence is a necessity in the origin of any informational code, including the genetic code, no matter how much time is given.”[23] Philosopher of Science and founder of the Discovery Institute, Dr. Stephen Meyer, writes, “Our uniform experience affirms that specified information-whether inscribed hieroglyphics, written in a book, encoded in a radio signal, or produced in a simulation experiment-always arises from an intelligent source, from a mind and not a strictly material process.”[24]
Thus, we are left with no natural method or process by which non-living chemicals can produce the informational code found in every life form that as ever existed. Biologist, Chemist and Physiologist Dr. Gary Parker writes, “Imagine that you have just finished reading a fabulous novel. Wanting to read another book like it, you exclaim to a friend, ‘Wow! That was quite a book. I wonder where I can get a bottle of that ink?’ Of course not! You wouldn’t give the ink and paper credit for writing the book. You’d praise the author, and look for another book by the same writer. By some twist of logic, though, many who read the fabulous DNA script want to give credit to the ‘ink (DNA base code) and paper (proteins)’ for composing the code.”[25]
Not Enough Time
With all things considered, many scientists try to jettison out the first life dilemma with the “time” argument. The argument being that given enough time anything can happen! Even the impossible…
The late Nobel prize winning scientist George Wald once wrote, “However improbable we regard this event [evolution], or any of the steps which it involves, given enough time it will almost certainly happen at least once… Time is in fact the hero of the plot… Given so much time, the ‘impossible’ becomes possible, the possible probable, the probable virtually certain. One has only to wait; time itself performs the miracles.”[26]
Now let us logically think about this. Given enough time, anything is possible? First, I feel pressed to point out that there is something irrational in saying that because something is possible, it will occur. Or anything that can happen, will happen. It is possible that in flipping a coin every minute for fifty years you will get heads every time and never tails… but that doesn’t mean it will happen if you tried. Regardless, the notion that given enough time anything can happen is hardly scientific in my opinion, because it flies in the face of observational science. For example, the Law of Biogenesis which firmly points out that life has only been observed coming from existing life, never from non-life. There is also cell theory, which states that cells arise from pre-existing cells. Regardless of the amount of time tacked onto the issue, the law cannot change, and the dimension of time has no characteristic capable of changing this law.
Let us take for example a chair placed in a room. The chair remains in the room for one hundred years, then a thousand years, and eventually billions of years. At any point would that chair become organic or “living” in anyway? Of course not. It would remain just a chair forever. Why? Because there is nothing inherent in non-living molecules that drive them to arrange themselves into living structures. If there were, they’d be doing so to this day at an observable rate. Such is not the case. Life comes from life, and non-life remains non-life everyday.
Another flaw in this argument is the amount of time in question. Such statements like Wald’s seem to have at least a small degree of plausibility in perhaps an infinite time scenario, but time is not infinite. It definitely had a starting point. A starting point which conventional scientists place at 12 to 14 billion years ago. That is a major constraint on how long time is allowed to work its magic. Cosmologist Dr. Hugh Ross writes, “When it comes to the origin of life, many biologists (and others) have typically assumed that plenty of time is available for natural processes to perform the necessary assembly. But discoveries about the universe and the solar system have shattered that assumption. What we see now is that life must have originated on earth quickly.”[27]
This constraint worsens though because conventional geology and biology places the first life forming 3.5 billion years ago, and the earth is only supposedly 4.5 billion years old. So from a naturalist’s or uniformitarian’s point of view there was a billion years from the time earth was formed to the first fossil evidence of life, from which life is said to have manifested. A billion years is a significant time constraint.
Yet, the time constraint worsens further. From a conventional scientist’s perspective adhering to the nebular hypothesis of sun and planet formation, time is further restricted. The first millions of years would have been one of intense meteorite bombardment of earth as the solar system was forming. These intense meteorite bombardments would have eradicated any chance of life forming on earth. By the time these impacts are calculated to have ceased and the time of the first life forms appearing in the fossil record we’re left with a 10 million year gap.[28] That is an enormous time constraint. Additionally, some scientists propose this time frame was shorter because of the “faint sun paradox.” Namely, that the sun was 20 to 30% less luminous when it first existed, creating a very cold inhospitable world.[29] This makes it difficult to apply Ward’s philosophy of an abundance of time making the impossible possible because there is, for lack of a better phrase, hardly any time at all…
In fact, Nobel Prize winning cytologist and biochemist Christian de Duve states, “It is now generally agreed that if life arose spontaneously by natural processes—a necessary assumption if we wish to remain within the realm of science—it must have arisen fairly quickly, more in a matter of millennia or centuries, perhaps even less.”[30] So much for having all the time in the world.
Lastly, I do feel it is necessary to point out the entropy dilemma when it comes to time. The more time that elapses the higher the entropy, so if anything more time doesn’t make anything possible, but in fact, decreases the potential of anything to happen. As biochemist Dr. Royal Truman writes, “The claim that, with time, anything is possible, including the creation and perpetuation of life, is not based on any scientific principle. Rather, the opposite is true: complex and improbable structures of any kind tend to disintegrate over time.”[31] Sarfati agrees, “Long time periods do not help the evolutionary theory if biochemicals are destroyed faster than they are formed.”[32]
Panspermia; DNA astronauts
The difficulty with life spontaneously arising via chemical means is such a problematic concept that it lead Nobel Prize winner and DNA founder Francis Crick to instead postulate that life originated someplace else and traveled to earth via meteorite or space craft.[33] He admits, correctly, that this does not solve the origin of life problem, but merely pushes it back to another location, but that is precisely the point. He proposes that another life bearing planet may have had a slightly different environment more hospitable for the natural chemical means for life to originate.[34] This theory relies on the hypothetical existence of other such life bearing planets to which there is no scientific evidence of, period.

There is additionally a whole host of other problems with Panspermia. How do living cells survive an arduously long space flight on a meteorite? Let us not forget how far away the nearest star is much less the nearest hypothetical life bearing planet. Think of how difficult it would be to create and engineer a capsule to keep living cells alive for thousands of years of space flight, yet a random natural meteorite is capable of doing the job? DNA would have succumb to radiation exposure over such a long period of time in space flight. How did the DNA withstand the lethal radiation? So, these same cells that defied death in thousands (if not millions) of years of freezing space exposed to lethal radiation then somehow survived a scorching hot entry into earth’s atmosphere to reproduce on earth’s surface? As chemist Russell Grigg puts it, “All in all, interstellar space travel for living organisms is sheer wishful thinking.”[35]
What about contamination? Many of the meteorites found on earth claimed to have evidence of microbial life could just have easily had been contaminated with microbial life after they landed. Contamination is the number one reason why all these claims have been rejected actually.
To get around these concerns, many scientists instead believe meteorites and comets didn’t have life per se, but had the building blocks of life on them. But this circles back around to the original reason why panspermia was imagined in the first place. The building blocks of life were already present on earth. Adding more to the mix via meteorites doesn’t in anyway increase the likelihood of life arising via chemical means anyways. Ross brings up another good point, “Though comets, meteorites partly composed of carbon, and interplanetary dust particles may carry some prebiotics, they carry far too few to make a difference. In fact, with every helpful molecule they bring, come several more that would get in the way- useless molecules that would substitute for the needed ones.”[36] Life developing from nonliving chemicals is hard enough to prove, but suggesting life was seeded by meteorites from hypothetical life elsewhere in the universe is flat out impossible to prove. Yet, likewise, impossible to disprove… and so many cling to this notion to avoid a supernatural cause.
From Bolts to Boeing 747s
Many scientists additionally fail to properly distinguish the building blocks of life and living organisms themselves. Parker writes, “The pyramids are made of stone, but studying the stone does not even begin to explain how the pyramids were built. Similarly, until evolutionists begin to explain the origin of the ‘orderly mechanism,’ they have not even begun to talk about the origin of life.”[37]Just as there is a huge void between the bolts and small parts of a 747 to them actually all being carefully assembled into a fully functioning 747, likewise, the simple building blocks of life are organized in an immensely complex way in even the most primitive of organisms.
Hoyle writes of this airplane analogy, “What are the chances that a tornado might blow through a junkyard containing all the parts of a 747, accidentally assemble them into a plane, and leave it ready for take off? The possibilities are so small as to be negligible even if a tornado were to blow through enough junkyards t fill the whole universe!”[38] Botanist Alexander Williams states, “There is an unbridgeable abyss below the autopoietic hierarchy, between the dirty, mass-action chemistry of the natural environment and the perfect purity, the single-molecule precision, the structural specificity, and the inversely causal integration, regulation, repair, maintenance and differential reproduction of life.”[39]
According to molecular biophysicist Harold Morowitz If you were to take a living cell, break every chemical bond within it so that all you are left with is the raw molecular ingredients, the odds of them all reassembling back into a cell (under ideal natural conditions) is one chance in 10100,000,000,000.[40] Additionally, Morowitz assumed all amino acids were bioactive when calculating these odds.[41] But only twenty different types of amino acids are bioactive, and of those, only left handed ones can be used for life. This further worsens the odds… And with odds like that, time is completely irrelevant because no amount of time could surpass before such an impossible miracle occurred naturally.
Non-theists counter argue that life was not necessarily as complex in the beginning as it is today. Therefore, the odds of a less complex form of life spontaneously assembling are much more probable. The problem with this counter argument is that the earth 3.5 billion years ago was supposedly hardly different at all (environment and atmosphere-wise) than earth today. Meaning the bare necessities required for life to exist on earth today were the same in the past, which is that of great complexity. Additionally minimum complexity presents its own problems in that minimally complex organisms require other larger organisms to survive and are not capable of surviving individually. Thus the first life and its subsequent offspring would have had to have been able to survive independently which requires sophisticated biological features.
Astronomer Michael Hart calculated the odds of DNA spontaneously generating with 100 specific genes (what he declared to be the minimum possible for life) in the most unrealistic yet optimistic conditions over the course of ten billion years. The odds? One in ten to the negative three thousandth power (10-3,000).[42] The time it would take for 200,000 amino acids to come together by chance to create one human cell would be 293.5 times the estimated age of earth of 4.6 billion years.[43] The Director of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Delaware, Dermott Mullan, calculates that the odds of RNA assembling into a primitive cell over the course of an optimistic 1 billion years is one in 1079.[44] Material scientist Dr. Walter Bradley and Chemist Dr. Charles Thaxton calculated that the probability of amino acids forming just one protein is 4.9 x 10-191.[45] The odds of amino acids coincidentally being in the precise order and folds required to make the all the enzymes required for life is 10-650.[46] These are all horrible odds for a natural origin of life. Then consider that these statistics are independent of each other; the DNA would have to spontaneously generate, amino acids randomly together to form proteins in a cell, RNA assembling into a cell, etc. It is hard to accept with these odds, that anything that can happen did happen.
The Reproduction Puzzle
The late philosopher Anthony Flew, an ex-atheist, spoke of many of the philosophical troubles he had with the natural origins for life. One of which that was of great concern was reproduction. Life evolving from non-life is already such a statistical impossibility, but if it did happen, this first life would have to be able to reproduce and replicate itself. Information encoded DNA capable of driving life derived from non-living chemicals is already an absurd concept, but to contain information for replication and overall reproduction is astounding. This is from a philosophical standpoint, perplexing. It is too perfect and too coincidental that the very first life, already an impossibility, just so happened to also be able to duplicate itself. Such ability has “design” written all over it, not “chance.”
Error Protection
Even the most primitive cells today have multiple checkpoints in place to protect against errors. Cells have DNA checkpoints, where cell function momentarily pauses for special proteins to repair damaged DNA. There is an apoptosis checkpoint right before mitosis begins where specialized proteins called survivins run a “diagnostics” to determine whether the cell will proceed with mitosis or die through apoptosis. A spindle assembly checkpoint ensures chromosomes are properly bound together. Telomeres burn like fuses every time a cell divides. Once a telomere becomes too short, the cell stops dividing, usually maxing out at fifty divides.[47] This feature controls cell division. Failure for these mentioned checkpoints to operate leads to a whole host of diseases, most notably cancers.[48]
So how did the first cell protect against errors when it reproduced? Such a capability could not have evolved, because such a capability would have been needed right from the very beginning. Without such a feature, all subsequent life would contain error-prone genetics and would not be able to function or reproduce. Mullan, points out, “A cell formed under these conditions [naturally] would truly be subject to serious uncertainties not only during day to day existence but especially during replication. The cell could hardly be considered robust.”[49] In order to maintain healthy function and reproduction, the first cell would have already needed these specialized checkpoints to guard against errors. The cells could not afford to wait thousands or millions of years for them to evolve. If they did, we wouldn’t be here.
Simultaneous Presence
In order to have fully functioning life at even the most basic kind, functioning RNA, DNA and proteins must be present. Remove any one of these from the picture and life can’t function. For example, transcription, translation and DNA replication all require systems already in place to occur. These functions could not simply have evolved because life requires them in place to begin with. As Ross states, “Thus, for life to originate mechanically, all three kinds of molecules [DNA, RNA, and proteins] would need to emerge spontaneously and simultaneously from organic compounds. Even the most optimistic of researchers agree that the chance appearance of these incredibly complex molecules at exactly the same time and place was beyond the realm of natural possibility.”[50]
Though biologists point out that some RNA has been found to act as enzymes or catalysts to perform functions that DNA or a protein would normally do, this has lead many scientists to propose that all one needs is the spontaneous generation of RNA, and it would take care of the rest. Problems with this theory is that the RNA studied to reveal these abilities was very limited, and could not account for the vast functioning seen in DNA and proteins overall. Furthermore, in order for RNA to function this way it would have to contain just as much information as the DNA and protein itself, so the issue of complexity in even the earliest life isn’t solved with RNA either. Molecular Biologist and professor at the Scripps Research Institute, Dr. Gerald F. Joyce writes, “The most reasonable interpretation is that life did not start with RNA … The transition to an RNA world, like the origins of life in general, is fraught with uncertainty and is plagued by a lack of relevant experimental data. Researchers into the origins of life have grown accustomed to the level of frustration in these problems …”[51]
Conclusion
Biologist Jonathan Wells just about sums it up, “So we remain profoundly ignorant of how life originated.”[52] Earth Scientist Casey Luskin writes, “It’s time for a little reality check here: origin-of-life theorists need to explain how a myriad of complex proteins and features arose and self-assembled into a self-replicating life-form by unguided processes, but they are still scraping for mechanisms to explain how an inert primordial soup of organic molecules could have arisen in the first place.”[53] Hoyle writes, “If there were some deep principle that drove organic systems towards living systems, the operation of the principle should easily be demonstratable in a test tube in half a morning. Needless to say, no such demonstration has ever been given. Nothing happens when organic materials are subjected to the usual prescription of showers of electrical sparks or drenched in ultraviolet light, except the eventual production of a tarry sludge,” and “As biochemists discover more and more about the awesome complexity of live, it is apparent that its chances of originating by accident are so minute that they can be completely ruled out. Life cannot have arisen by chance.”[54] Physicist and Information Theorist Dr. Hubet Yockey writes, “The origin of life by chance in a primeval soup is impossible in probability in the same way that a perpetual machine is in probability. The extremely small probabilities calculated… are not discouraging to true believers . . . [however] A practical person must conclude that life didn’t happen by chance.”[55]
Yockey then goes further to add, “The history of science shows that a paradigm, once it has achieved the status of acceptance (and is incorporated in textbooks) and regardless of its failures, is declared invalid only when a new paradigm is available to replace it. Nevertheless, in order to make progress in science, it is necessary to clear the decks, so to speak, of failed paradigms. This must be done even if this leaves the decks entirely clear and no paradigms survive. It is a characteristic of the true believer in religion, philosophy and ideology that he must have a set of beliefs, come what may… Belief in a primeval soup on the grounds that no other paradigm is available is an example of the logical fallacy of the false alternative. In science it is a virtue to acknowledge ignorance. This has been universally the case in the history of science… There is no reason that this should be different in the research on the origin of life.”[56] Biochemist and head of the Department of Nuclear Medicine and Director of Clinical Research at the Singapore General Hospital, Dr. Aw Swee-Eng, concludes, “The available evidence from the field and the laboratory is not amicable to the theory that life began with the accidental assembly of a self-replicating molecule.”[57]

As it has been clearly demonstrated, there are a wide variety of blockades standing in the way of a natural origins answer for the first life, and no definitive solution has been reached nor can be confidently expected to be reached in the future. Yet, the other option, supernatural origins, is not subject to such obstacles. In fact, every problem a natural origin faces can be satisfactorily answered via supernatural origins. Though many scientists will not appeal to super natural intervention on the grounds that it is not science, and merely a “cut and run” for those who are too impatient to wait for future researchers to provide an adequate natural origins argument.
In response to that notion, Denton answers, “The almost irresistible force of the analogy has completely undermined the complacent assumption, prevalent in biological circles over most of the past century, that the design hypothesis can be excluded on the grounds that the notion is fundamentally a metaphysical a priori concept and therefore scientifically unsound. On the contrary, the inference to design is a purely a posteriori induction based on a ruthlessly consistent application of the logic of analogy. The conclusion may have religious implications, but it does not depend on religious presuppositions.”[58] Therefore, adhering to supernatural cause through rational deduction with proper observational science as support cannot be considered unscientific. Additionally, such a conclusion should not be considered a “cut and run” if the problems faced by natural origins can never be solved via natural means. What discovery (or discoveries) could solve the information, reproduction, environment, homochirality problems?
Physicist H. S. Lipson writes, “If living matter is not, then, caused by the interplay of atoms, natural forces, and radiation [i.e., time, chance, and chemistry], how has it come into being? I think, however, that we must go further than this and admit that the only acceptable explanation is creation.”[59] Parker writes, “In a novel, the ink and paper are merely the means the author uses to express his or her thoughts. In the genetic code, the DNA bases and proteins are merely the means God uses to express His thoughts. The real credit for the message in a novel goes to the author, not the ink and paper, and the real credit for the genetic message in DNA goes to the Author of Life, the Creator…”[60] Medical pathologist David Demick, M.D., concludes, “Thousands of experiments, and all of the recently gained knowledge of molecular biology and genetics, have only served to strengthen the most fundamental law of biology, laid down by Virchow over a century ago: ‘omni cellules e cellules’ (all cells come from other cells), also known as the Law of Biogenesis. Life only comes from life. This was the law established by the Author of Life, Who is the Way, the Truth, and the Life—Jesus Christ.”[61] Griggs concludes, “Life is bristling with machinery, codes and programs, which are not an inherent property of the material substrate (the information for their construction having been passed on during reproduction). No observation has ever shown such information-bearing structures arising spontaneously. The obvious inference from science, as well as the obvious implications of Scripture, is that the original creation of living things involved the very opposite of chance, namely, the imposition of external intelligence on to matter by an original Designer or Creator.”[62]
So we’re left with a choice. Supernatural or natural? One answers all these problems, the other does not. You can hold out for a natural answer if you wish, but I would rather side with a sure thing. Logically, an Intelligent Designer, a God, is in my opinion, the only rational explanation behind the first life.
[1] Ward, P. & Brownlee, D., (2000) Rare Earth, Copernicus:New York,NY, pp. 245.
[2] Clemmey, H. & Badham, N., (1982) “Oxygen in the Atmosphere: An Evaluation of the Geological Evidence,” Geology, 10:141.
[3] Thaxton, C.B., Bradley, W.L., & Olsen, R.L., (1984) The Mystery of Life’s Origin: Reassessing Current Theories, Philosophical Library:New York,NY, pp. 69-98.
[4] Trail, D., Watson, B.E., & Tailby, N.D., (December 2011) “The Oxidation State of Hadean Magmas and Implications for Earth’s Early Atmosphere,” Nature, 480: pp. 79-82.
[5] Riddle, M., (2008) “Can Natural Processes Explain the Origin of Life?” as written in Ken Ham’s The New Answers Book 3, Master Books:Green Forest,AR, pp. 66.
[6] Denton, M., (1985) Evolution: A Theory in Crisis, Alder & Alder:Bethesda,MD, pp. 261.
[7] Riddle, M., (2008) “Can Natural Processes Explain the Origin of Life?” as written in Ken Ham’s The New Answers Book 3, Master Books:Green Forest,AR, pp. 66.
[9] Morris, R., (2002) The Big Questions, Times Books/Henry Holt:New York,NY, pp. 167.
[12] Sarfati, J., “15 Loopholes in the Evolutionary Theory of the Origin of Life,” creation.com
[13] Sarfati, J., (2002) Refuting Evolution 2, Master Books:Green Forest,AR, pp. 157.
[15] Riddle, M., (2008) “Can Natural Processes Explain the Origin of Life?” as written in Ken Ham’s The New Answers Book 3, Master Books:Green Forest,AR, pp. 67.
[16] Ashton, J., (2000) In Six Days, Master Books:Green Forest,AR, pp. 82.
[17] Pauling, L., (1970) General Chemistry, 3rd Ed., W.H. Freeman & Co.:San Francisco,CA, pp. 774.
[18] Shapiro, R., (1986) Origins: A Skeptic’s Guide to the Creation of Life on Earth, Summit Books:New York,NY, pp. 86.
[19] Swee-Eng, A., “The Origin of Life; a Critique of Current Scientific Models,” creation.com
[20] Gitt, W., “Dazzling Design in Miniture: DNA Information Storage,” creation.com
[22] Gitt, W., (2006) In The Beginning Was Information, Master Books:Green Forest,AR.
[23] Lester, L. & Bohlin, R., (1989) The Natural Limits To Biological Change, Probe Books:Dallas,TX, pp. 157.
[24] Meyer, S., (2009) Signature in the Cell, Harper Collins:New York,NY, pp. 347
[26] Wald, G., (1954) “The Origin of Life,” Scientific American, 191 no. 2:48.
[27] Ross, H., (1994) The Creator and the Cosmos, Navpress:Colorado Springs,CO, pp. 137.
[28] Ross, H., (1994) The Creator and the Cosmos, Navpress:Colorado Springs,CO, pp. 138.
[30] Duve, C., (September-October 1995) “The Beginnings of Life on Earth,” American Scientist, pp. 428.
[31] Truman, R., (December 2001) “The Fish in the Bathtub,” Creation
[32] Sarfati, J., “15 Loopholes in the Evolutionary Theory of the Origin of Life,” creation.com
[34] Crick, F., (October 1981) “The Seeds of Life,” Discover Magazine
[35] Grigg, R., (September 2000) “Did Life Come to Earth From Outerspace?” Creation, 22:(4), pp. 42
[36] Ross, H., (1994) The Creator and the Cosmos, Navpress:Colorado Springs,CO, pp. 138-139.
[38] As quoted in Paul E. Little’s Know Why You Believe, 4th Ed., InterVarsity Press:Downers Grove,IL, pp. 26.
[39] Williams, A., (August 2007) “Life’s Irreducible Structure- Part 1: Autopoiesis,” Journal of Creation, 21:(2) pp. 115.
[40] Shapiro, R. (1986) Origins: A Skeptic’s Guide to the Creation of Life on Earth, Summit Books:New York,NY, pp. 128.
[41] Ross, H., (1994) The Creator and the Cosmos, Navpress:Colorado Springs,CO, pp. 141.
[42] Hart, M. H. (1990) “Atmospheric Evolution, the Drake Equation, and DNA: Sparse Life in an Infinite Universe,” Physical Cosmology and Philosophy, MacMillan:New York,NY, pp. 264.
[43] Little, P.E., (2000) Know Why You Believe, 4th Ed.,InterVarsity Press:Downers Grove,IL, pp. 26.
[45] Thaxton, C., Bradley, W., & Olsen, R., (1984) The Mystery of Life’s Origins: Reassessing Current Theories, Philosophical Library:New York,NY, pp. 80.
[46] Sarfati, J., “15 Loopholes in the Evolutionary Theory of the Origin of Life,” creation.com
[47] Lewis, R., (2008) Human Genetics; Concepts and Applications, 8th Ed., McGraw Hill:New York,NY, Pp. 30-31.
[48] Lewis, R., (2008) Human Genetics; Concepts and Applications, 8th Ed., McGraw Hill:New York,NY, Pp. 355.
[50] Ross, H., (1994) The Creator and the Cosmos, Navpress:Colorado Springs,CO, pp. 142.
[51] Joyce, G.F., (1989) “RNA Evolution and the Origins of Life,” Nature 338: pp. 222-223
[52] Wells, J., (2000) Icons of Evolution, Regnery Publishing:WashingtonD.C., pp. 24.
[54] Hoyle, F., (1983) The Intelligent Universe, Michael Joseph:London, pp. 251.
[55] Yockey, H.P., (1992) Information Theory and Molecular Biology, CambridgeUniversity Press:UK, pp. 257.
[56] Yockey, H.P., (1992) Information Theory and Molecular Biology, CambridgeUniversity Press:UK, pp. 336.
[57] Swee-Eng, A., “The Origin of Life; a Critique of Current Scientific Models,” creation.com
[58] Denton, M., (1986) Evolution: A Theory in Crisis,3rd Ed., Alder & Alder, pp. 341.
[59] Lipson, H. S., (May 1980) “A Physicist Looks at Evolution,” Physics Bulletin, pp. 138.
[61] Demick, D., (December 2000) “Life From Non-Life… or Not?” Creation 23:1 pp. 41.
[62] Grigg, R., (December 1990) “Could Monkeys Type the 23rd Psalm?” Creation 13:1 pp. 34












